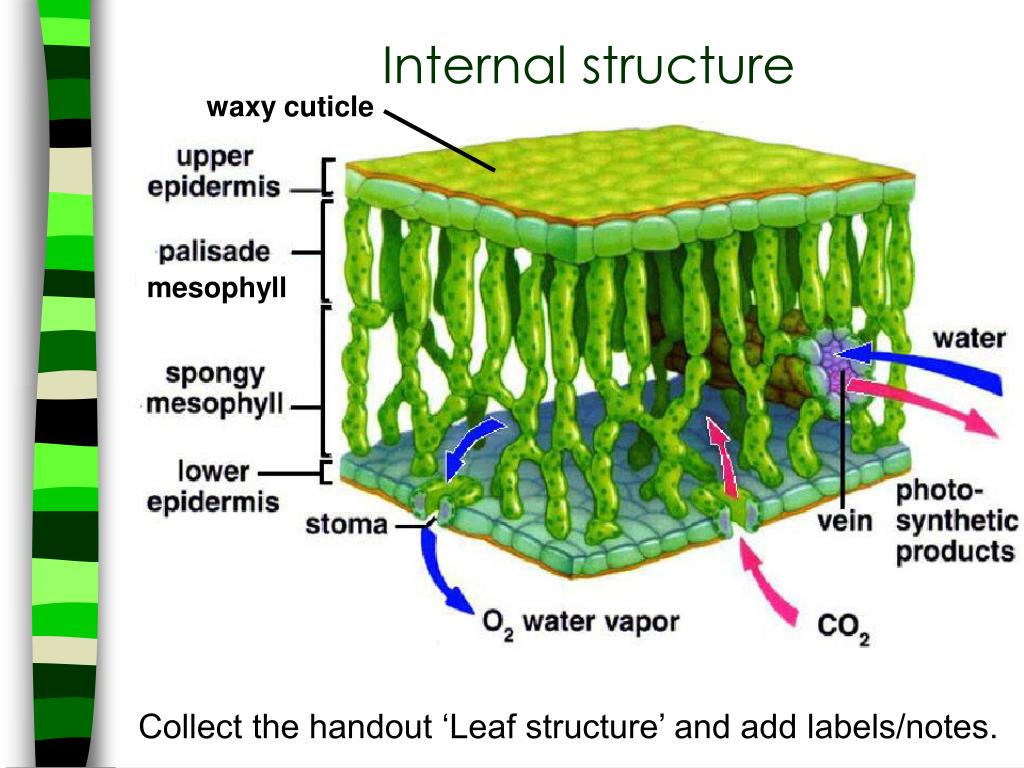
39 label the internal parts of the chloroplast below
Chloroplast: Meaning, Structure, Analogy - Embibe The diagram of Chloroplast is given below. Fig: A Labeled Diagram of Chloroplast. Chloroplast Structure Chloroplasts are roughly \(1 - 2\, {\rm{μm}}\) thick and \(5 - 7\, {\rm{μm}}\) in diameter and are seen in all higher plants. In different plants, chloroplasts have different shapes like some plants have filamentous or ovoid or saucer ... Labeling Parts to a Chloroplast Diagram - Quizlet Labeling Parts to a Chloroplast STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by Abby_Larson72 Terms in this set (5) outer membrane ... inner membrane ... stoma ... granum stack of thylakoids thylakoid ... YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE... Science test 10 Terms Caycay666 Parts and Functions of the Chloroplast 8 Terms lamottas
Biology for Kids: Plant Cell Chloroplasts - Ducksters Chloroplasts are unique structures found in plant cells that specialize in converting sunlight into energy that plants can use. This process is called photosynthesis . Chloroplasts are considered organelles in plant cells. Organelles are special structures in cells that perform specific functions. The main function of the chloroplast is ...

Label the internal parts of the chloroplast below
Join LiveJournal Password requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols; Lifestyle | Daily Life | News | The Sydney Morning Herald The latest Lifestyle | Daily Life news, tips, opinion and advice from The Sydney Morning Herald covering life and relationships, beauty, fashion, health & wellbeing Chloroplasts Definition, Structure, Function and Microscopy Compared to other organelles, chloroplasts have three types of membranes that serve different functions. These include: The smooth outer membrane (outer envelope membrane) The smooth inner membrane (inner envelope membrane) Thykaloid membrane system
Label the internal parts of the chloroplast below. Chloroplast: Structure and Function - Biology Wise The major components of a chloroplast are as illustrated and explained below. Envelope The chloroplast envelope is double-membrane structure comprising an outer and an inner membrane. Each of these membranes is a phospholipid bilayer, and is 6 - 8 nm thick. A 10 - 20 nm thick space present between the two membranes is known as intermembrane space. PDF 8.2 Photosynthesis: An Overview - Weebly 4. Chloroplasts contain an abundance of saclike photosynthetic membranes called . 5. The is the fluid portion of the chloroplast located outside the thylakoids. 6. The visible light absorbed by chlorophyll the energy level of the chlorophyll's electrons. 7. Label the internal parts of the chloroplast below. High-Energy Electrons Chloroplast Structure and Function in detail with Labelled Diagram The main components of a chloroplast are protein (50 to 60%), lipids, pigments like carotenoids and chlorophyll, a small amount of RNA and DNA, traces of Vitamin E and K and minerals iron, magnesium, manganese, etc. A chloroplast is covered by a membranous envelope, inside which matrix and thylakoids are present. Chloroplasts: Definition, Diagram, Structure and Function The diagram of the chloroplast given below represents the chloroplast structure including the different parts of the chloroplast. The parts of a chloroplast such as the inner membrane, outer membrane, intermembrane space, thylakoid membrane, stroma, and lamella are all mentioned. Diagram of Chloroplast Read Also Structure of Chloroplasts
Collins - Concise Revision Course For CSEC Biology | PDF ... Figure 5.1 Structure and function of the parts of a generalised animal cell. 5 Cells 33 cell wall – a freely permeable wall made of cellulose. Supports and protects the cell, and gives it shape cell membrane chloroplast – a disc-shaped organelle surrounded by a double membrane. The stroma is the fluid portion of the chloroplast - Course Hero Label the internal parts of the chloroplast below. Stroma Thylakoid granum Term Definition How I'm Going to Remember the Meaning Chlorophyll Primary pigment in plants. Chlorophyll gives plants their green color. Light- dependent reactions Light- independent reactions NADP+ Pigment StromaTHINK VISUALLY Thylakoid 120 Chloroplast Function in Photosynthesis - ThoughtCo Photosynthesis occurs in eukaryotic cell structures called chloroplasts. A chloroplast is a type of plant cell organelle known as a plastid. Plastids assist in storing and harvesting needed substances for energy production. A chloroplast contains a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis.Hence, the name chloroplast indicates that these structures are ... DOC 013368718X_CH08_115-128.indd - tesd.net 4. Chloroplasts contain an abundance of saclike photosynthetic membranes called . thylakoids. 5. The . stroma. is the fluid portion of the chloroplast located outside the thylakoids. 6. The visible light absorbed by chlorophyll . raises. the energy level of the chlorophyll's electrons. 7. Label the internal parts of the chloroplast below ...
Chloroplasts - Structure And Functions - A Level Biology Intermembrane Space - It is usually a thin intermembrane space about 10-20 nanometers and it is present between the outer and the inner membrane of the chloroplast. Inner membrane - The inner membrane of the chloroplast forms a border to the stroma. It regulates passage of materials in and out of the chloroplast. chloroplast | Definition, Function, Structure, Location, & Diagram They are enclosed in a chloroplast envelope, which consists of a double membrane with outer and inner layers, between which is a gap called the intermembrane space. A third, internal membrane, extensively folded and characterized by the presence of closed disks (or thylakoids ), is known as the thylakoid membrane. Life Processes Class 10 Extra Questions with Answers Science ... Aug 24, 2021 · It takes place in grana of chloroplast. Question 7. Define dark reaction. Answer: A chemical reaction, which can take place even in the absence of light, is called a dark reaction or light independent reaction. It takes place in stroma of chloroplast. Question 8. what are peristalic movements? Answer: PDF Bio 10: Ch 8.2 Photosynthesis: An Overview Label the internal parts of the chloroplast below. High-Energy Electrons For Questions 8-9, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing electron carriers to oven mitts. 8. In the visual analogy of carrying electrons, what represents the high- energy electrons? 9. Write another analogy that describes the process of electron carriers. 10.
Chloroplast- Diagram, Structure and Function Of Chloroplast The chloroplast structure consists of the following parts: Membrane Envelope It comprises inner and outer lipid bilayer membranes. The inner membrane separates the stroma from the intermembrane space. Intermembrane Space The space between inner and outer membranes. Thylakoid System (Lamellae) The system is suspended in the stroma.
7 Label the internal parts of the chloroplast below An Overview of ... 7. Label the internal parts of the chloroplast below. An Overview of Photosynthesis For Questions 11-13, write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 8. What are the reactants of the photosynthesis reaction?
PDF 8.2 Photosynthesis: An Overview Chloroplasts contain an abundance of saclike photosynthetic membranes called . 4. The is the fluid portion of the chloroplast located outside the thylakoids. 5. Label the internal parts of the chloroplast below. THINK VISUALLY Overview of Photosynthesis For Questions 6-8, write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 6.
PDF 8.2 Photosynthesis: An Overview - Mr. Insua's Science Site Label the internal parts of the chloroplast below. An Overview of Photosynthesis For Questions 11-13, write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 8. What are the reactants of the photosynthesis reaction? A. chlorophyll and light C. carbohydrates and oxygen B. carbon dioxide and water D. high-energy electrons and air 9.
Chloroplast - Definition, Function and Structure | Biology Dictionary Chloroplast Definition. The chloroplast, found only in algal and plant cells, is a cell organelle that produces energy through photosynthesis.The word chloroplast comes from the Greek words khloros, meaning "green", and plastes, meaning "formed".It has a high concentration of chlorophyll, the molecule that captures light energy, and this gives many plants and algae a green color.
biology honors: chapter 8 Flashcards - Quizlet true. true/false: the energy in food originally came from ATP. false: sunlight. true/false: the term photosynthesis means "pulling apart with light" in Greek. false: putting together. true/false: the energy of sunlight is stored in the chemical bonds of carbohydrates. true. the _______ of light determines it's color.
Chloroplasts- Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram The chloroplast has an inner and outer membrane with an empty intermediate space in between. Inside the chloroplast are stacks of thylakoids, called grana, as well as stroma, the dense fluid inside of the chloroplast. These thylakoids contain the chlorophyll that is necessary for the plant to go through photosynthesis.
Structure of Chloroplast (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion This will help you to draw the structure and diagram of chloroplast. 1. Chloroplasts (Figs. 295-296), responsible for the photosynthesis of the plants, are the characteristic features of the cells of green plants. ADVERTISEMENTS: 2. Around the chloroplast is present a double membrane envelope. 3. Each membrane of chloroplasst is 35 to 50 Å thick.




Post a Comment for "39 label the internal parts of the chloroplast below"