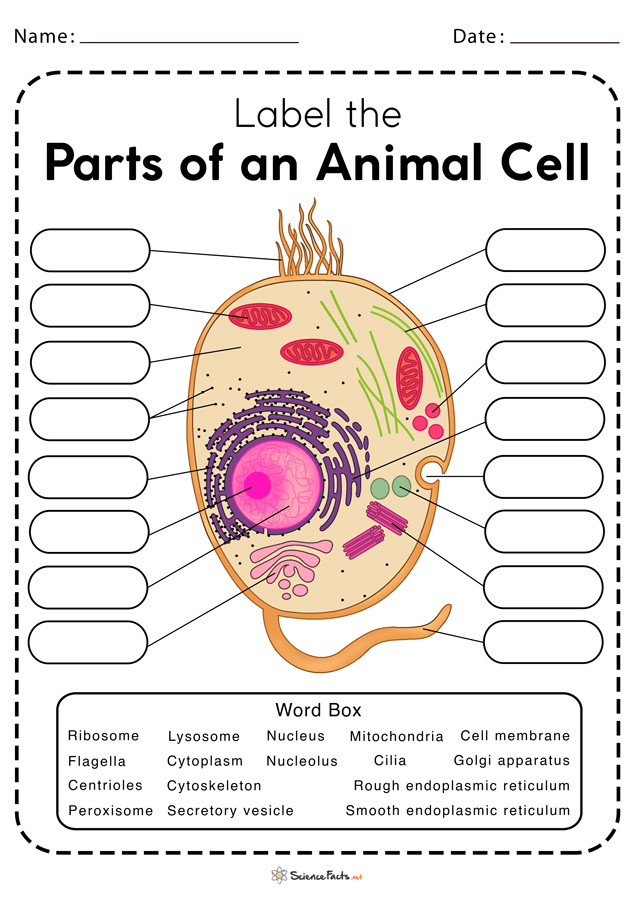
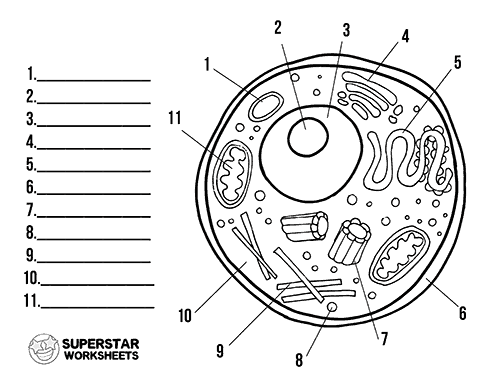
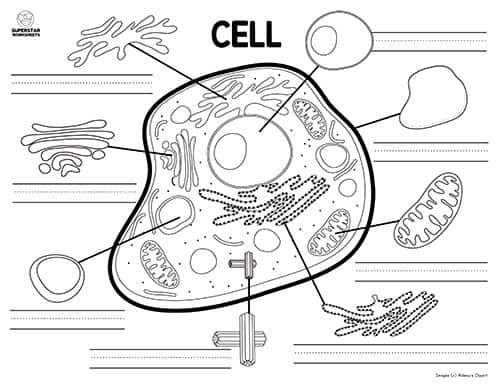
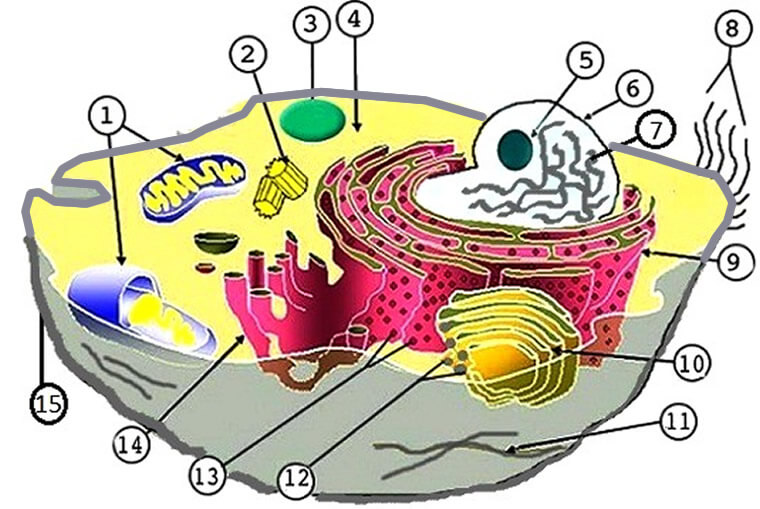
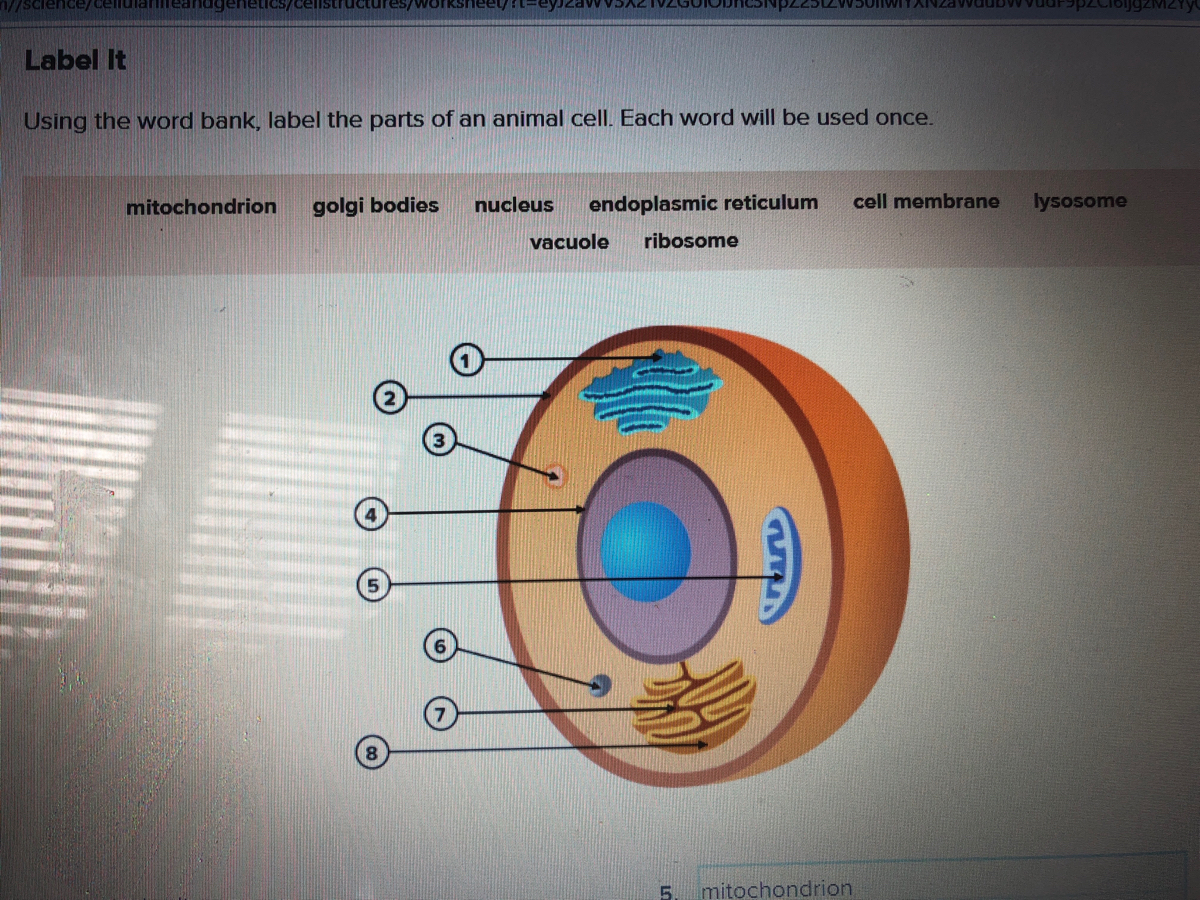
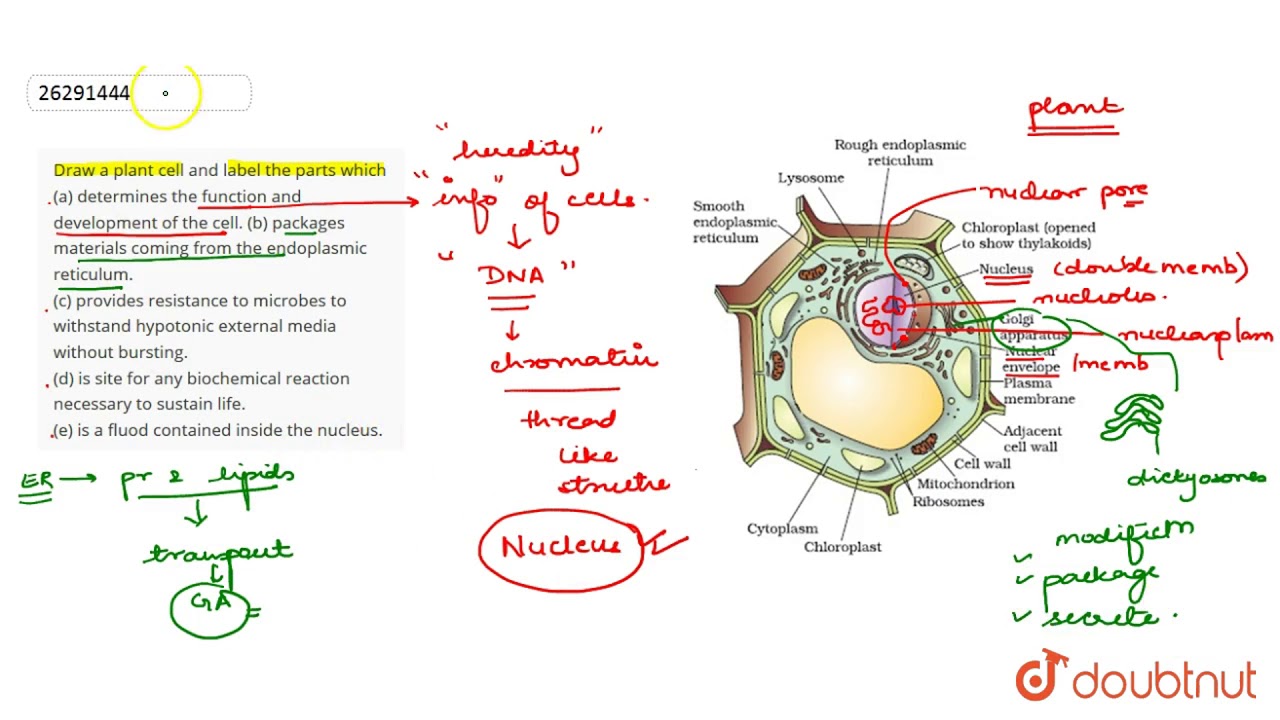
45 label parts of a cell
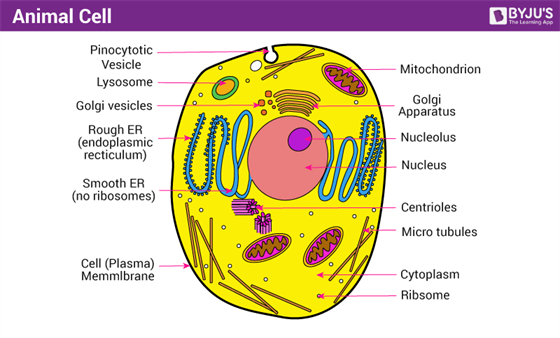
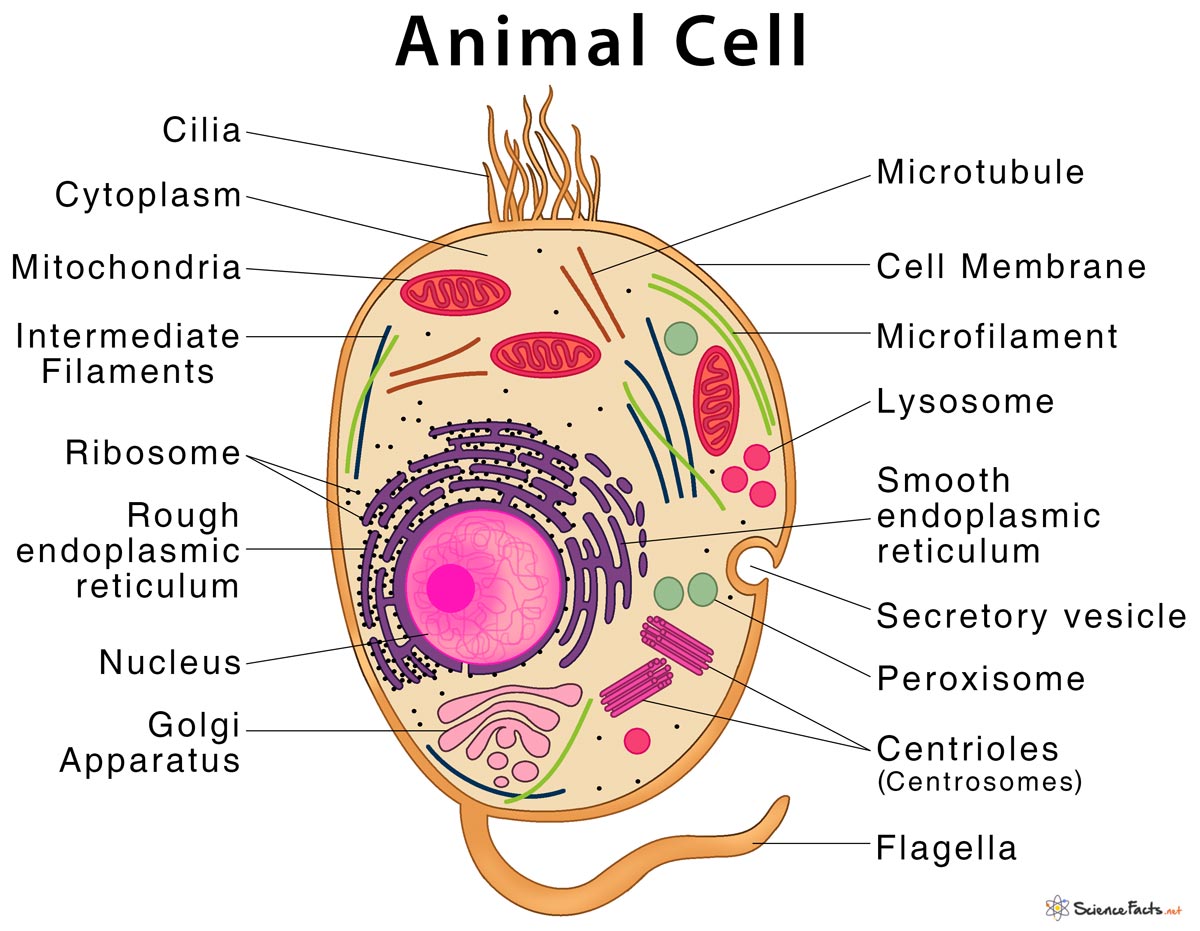
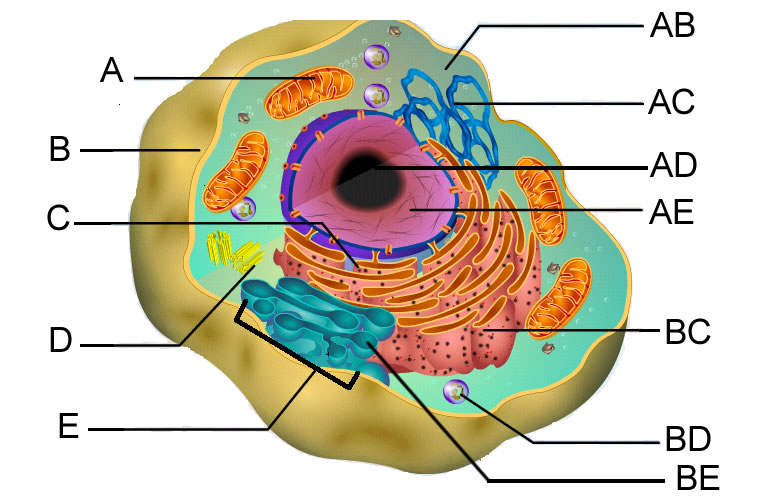
Free Anatomy Quiz - The anatomy of the cell - Quiz 1 centrioles, the cytoplasm, the rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulums, the golgi complex, lysosomes, microfilaments, mitochondria, the nucleolus, the nucleus, the nuclear membrane, pinocytotic vesicles, the plasma membrane, ribosomes and vacuoles. Take your knowledge of the cell further with our cell physiology quizzes : Quiz 1 --- Quiz 2 Label a cell, Labeling parts of a cell, Cells Structures and Functions ... Chloroplast Definition Where photosynthesis occurs to make oxygen and glucose, only found in plant cells Location Term Ribosome Definition Makes protein Location Term Mitochondria Definition Makes ATP (energy) through cellular respiration, power house of the cell Location Golgi body (label) nucleus (label) endoplamic reticulum (label)
Cell parts and functions (article) | Khan Academy Cells contain parts called organelles. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. A cell's organelles work alone and together to keep the whole cell functioning. Mitochondria are organelles that break down sugars. This process releases energy that the cell can use. The nucleus is an organelle that contains a cell's genes.
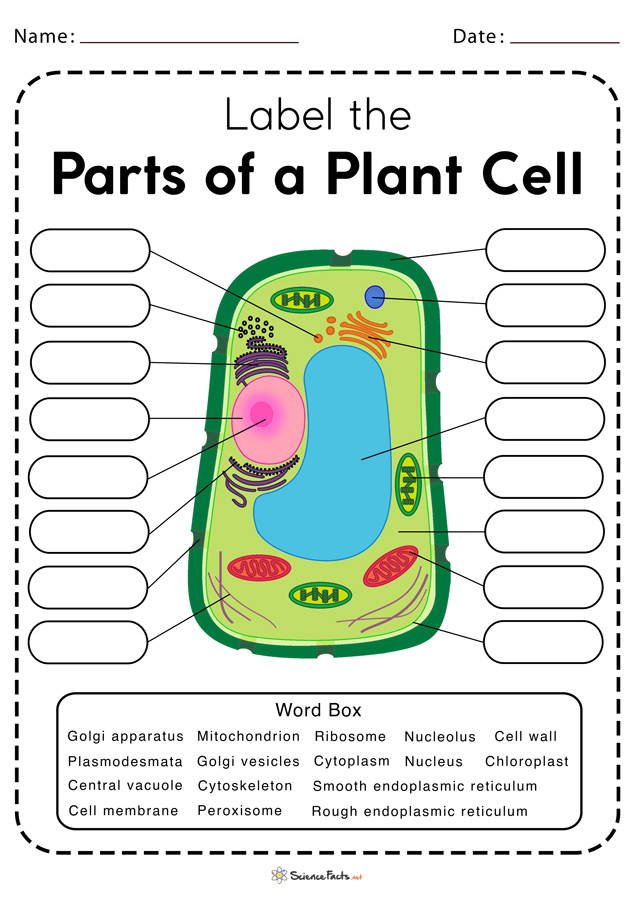
Label parts of a cell
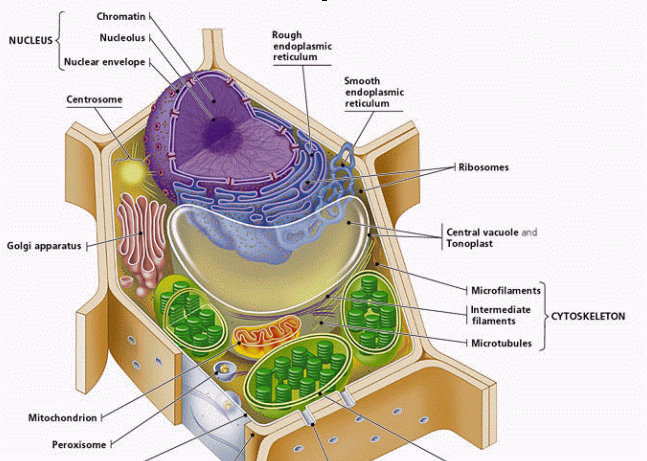
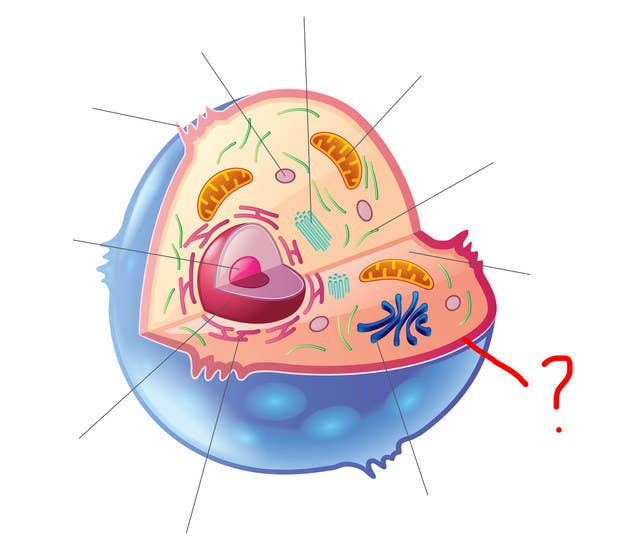
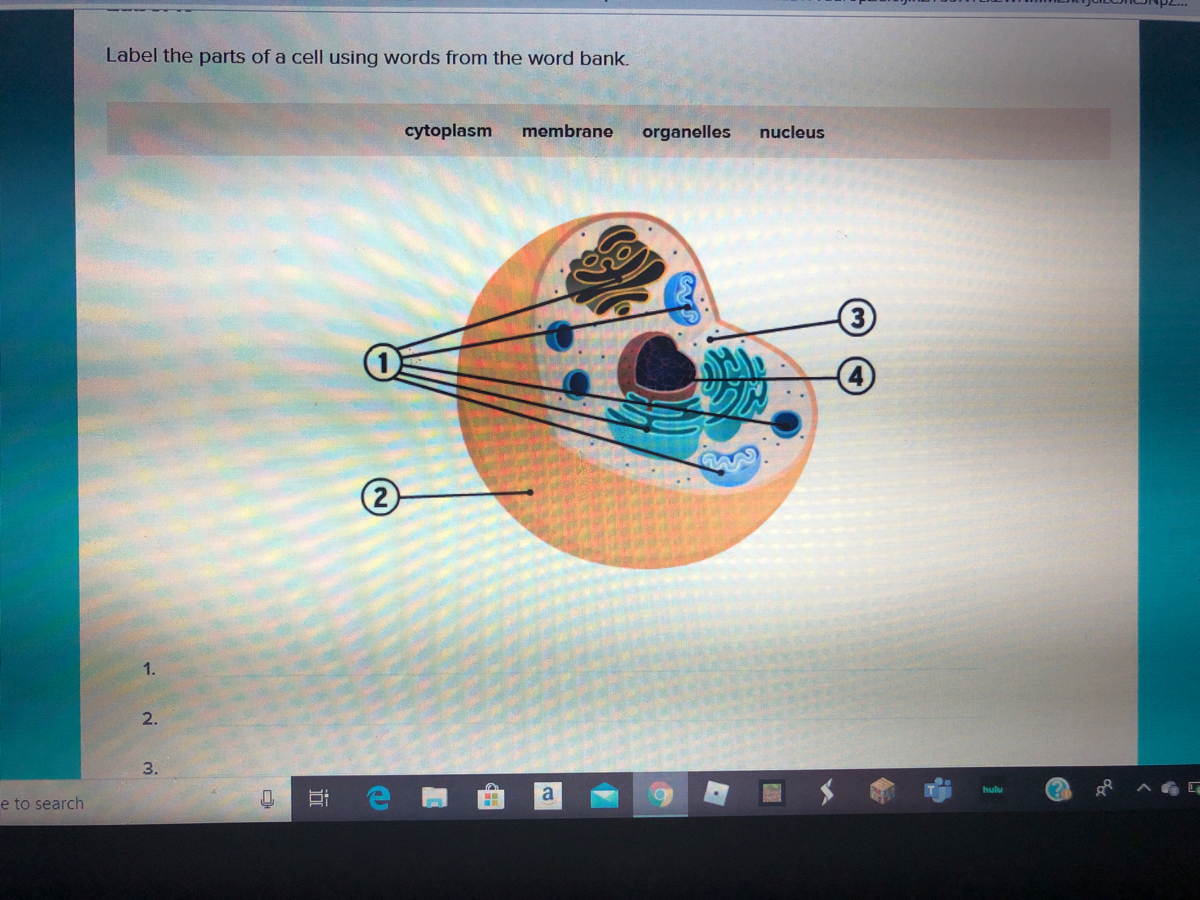
Labeling a Cell Diagram | Quizlet The command center of the cell. It controls cell's activity. Location Term Cytoplasm Definition A jelly-like substance that fills the cell. All of the cell's organelles are located here. Location Term Vacuoles Definition The storage facilities for the cell. They store food or waste that will be used of gotten rid of later. Cellular organelles and structure (article) | Khan Academy There are two main types of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotes are cells that do not have membrane bound nuclei, whereas eukaryotes do. The rest of our discussion will strictly be on eukaryotes. Think about what a factory needs in order to function effectively. Nucleus and ribosomes (article) | Khan Academy The nucleus. The nucleus (plural, nuclei) houses the cell's genetic material, or DNA, and is also the site of synthesis for ribosomes, the cellular machines that assemble proteins. Inside the nucleus, chromatin (DNA wrapped around proteins, described further below) is stored in a gel-like substance called nucleoplasm.
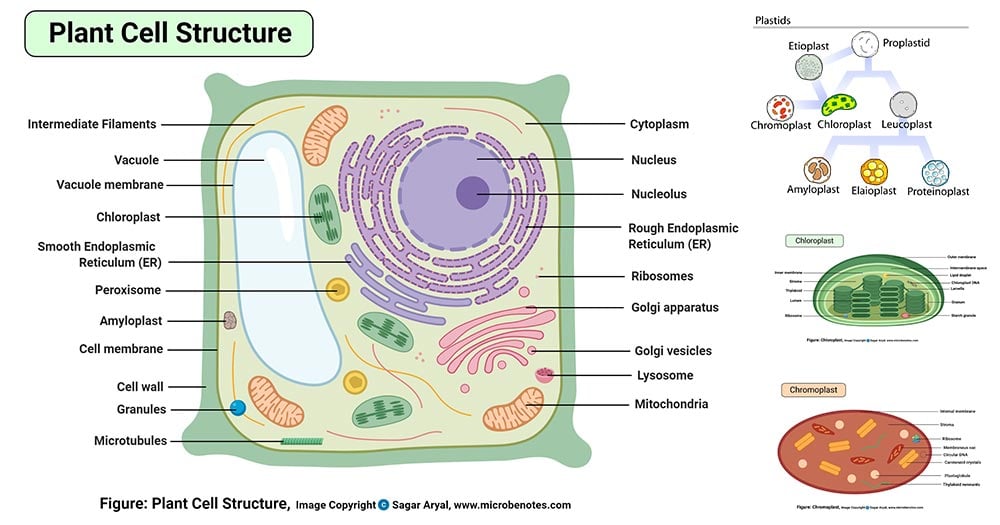
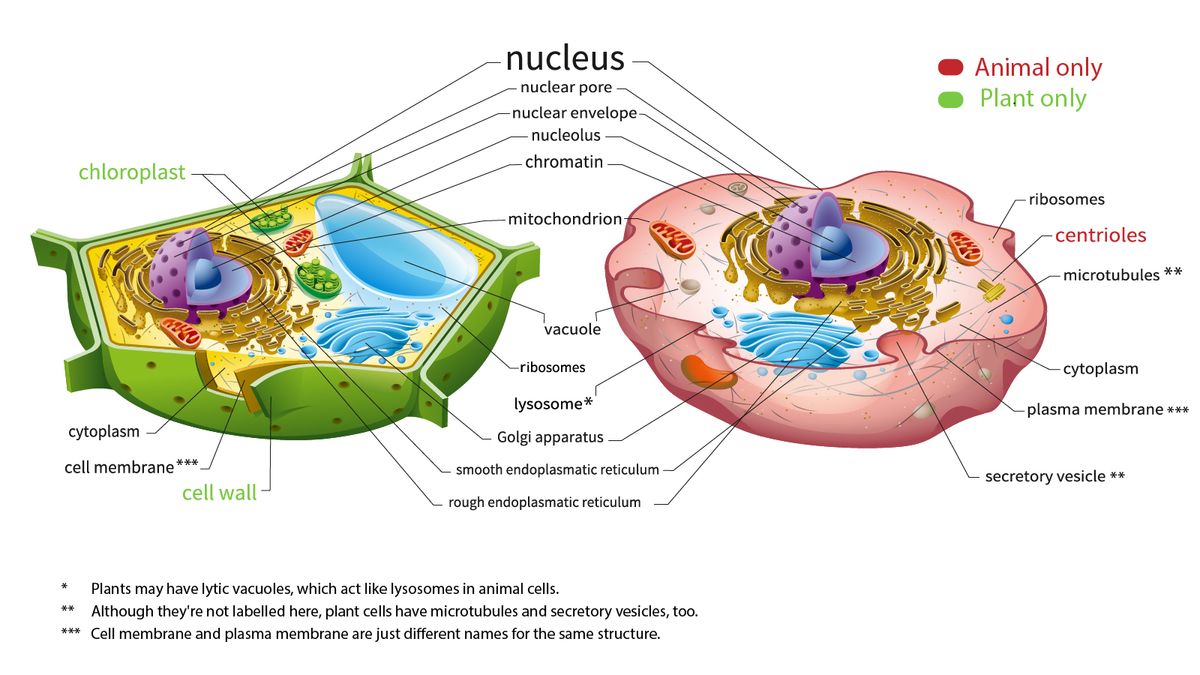
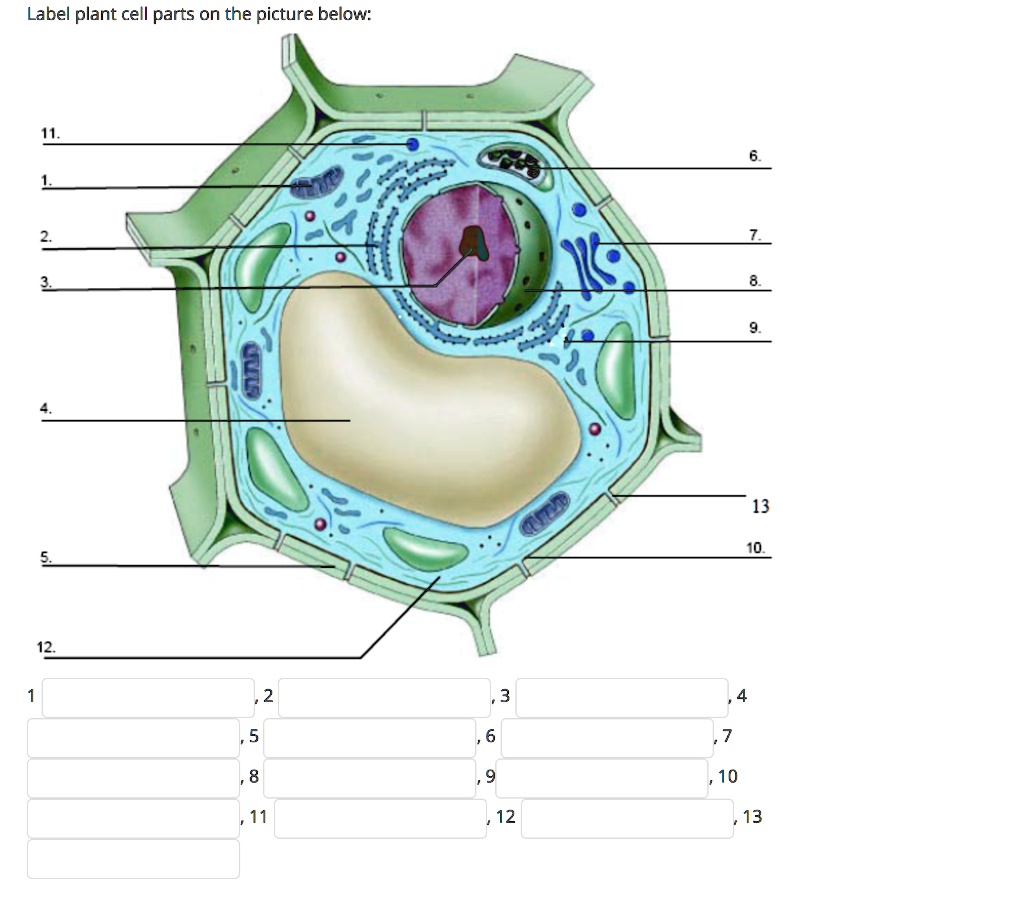
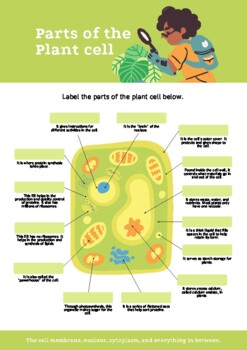
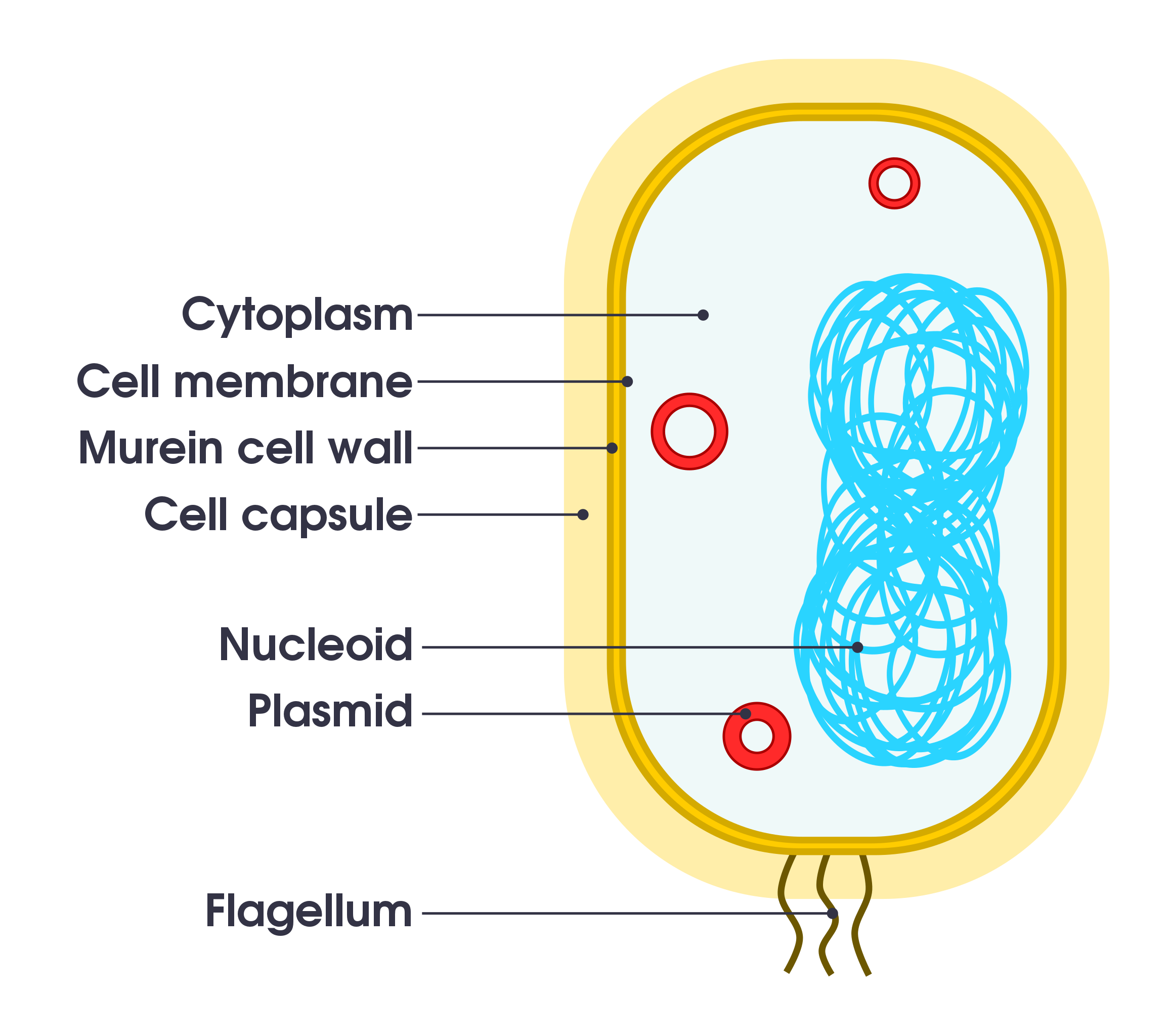
Label parts of a cell. Learn the parts of a cell with diagrams and cell quizzes There exist two general classes of cells: Prokaryotic cells: Simple, self-sustaining cells (bacteria and archaea) Eukaryotic cells: Complex, non self-sustaining cells (found in animals, plants, algae and fungi) In this article, we'll be focusing on eukaryotic cells. Two major regions can be found in a cell. Plant cell | Definition, Characteristics, & Facts | Britannica plant cell, the basic unit of all plants. Plant cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning they have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. The following is a brief survey of some of the major characteristics of plant cells. For a more in-depth discussion of cells, see cell. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. Although often perceived as an ... Cell Labeling: Definition, Methods, Types & Diagram Cell labelling refers to the visualisation of cells and the identification of cellular structures such as organelles. Cells can be labelled in multiple ways. These include using fluorescent dyes, immunolabeling and using fluorescent fusion proteins. Parts of a Cell Quiz | Britannica Parts of a Cell Quiz Question: What are the sites of protein synthesis? Answer: Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis. Question: What is the site of photosynthesis in a plant cell? Answer: A chloroplast is the site of photosynthesis in a plant cell. Question: Within a cell, what is a space that is empty of cytoplasm, lined with a membrane, and filled with fluid?
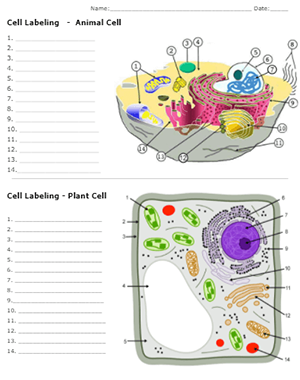
Identifying cell structures (practice) | Khan Academy Lesson 2: Basic cell structures. Introduction to the cell. Introduction to cilia, flagella and pseudopodia. Basic cell structures review. Identifying cell structures. Basic cell structures. Science >. High school biology >. Cell | Definition, Types, Functions, Diagram, Division, Theory, & Facts ... A cell is enclosed by a plasma membrane, which forms a selective barrier that allows nutrients to enter and waste products to leave. The interior of the cell is organized into many specialized compartments, or organelles, each surrounded by a separate membrane. Label Cell Parts | Plant & Animal Cell Activity | StoryboardThat What are the parts of a plant cell? A correct poster of a plant cell with labels would include: cell membrane, mitochondria, nucleus, ribosome, cytoplasm, cell wall, vacuole, and chloroplast. What are the parts of an animal cell? When plant and animal cells are labeled, they have very similar parts. Cell Parts and Functions | Biology Dictionary Usually, a cell has a single nucleus that contains all of its DNA molecules, but some (such as skeletal muscle cells) have more than one nucleus. The nucleus protects the cell's DNA while controlling all other cellular activities, such as cell division, growth, protein production, and cell death. The nucleus contains all the DNA of a cell Ribosomes
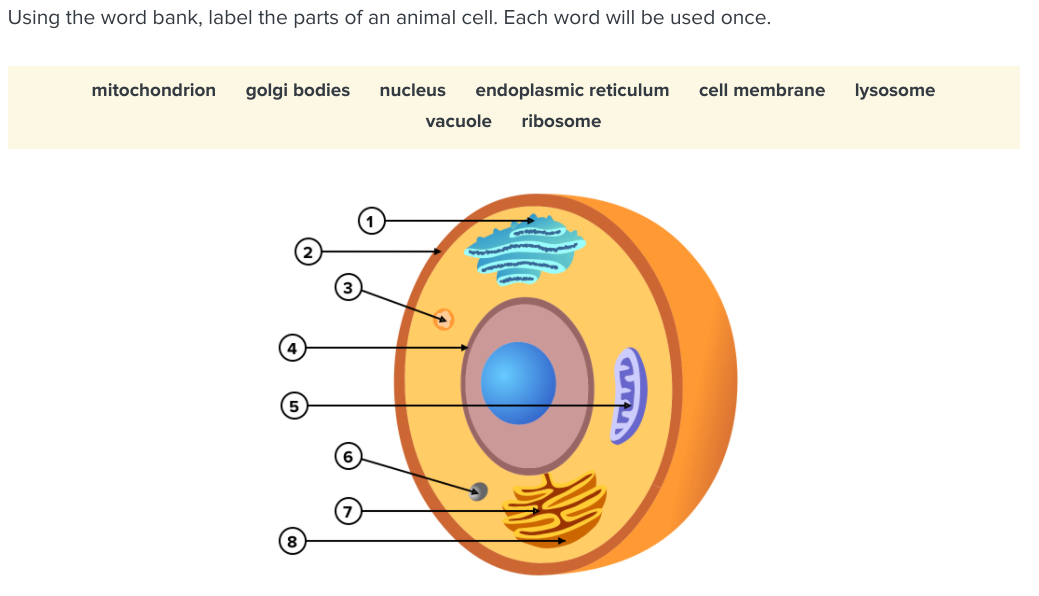
Label Animal And Plant Cells Teaching Resources | TPT The practice sheet helps to prep for the lab. These are editable and perfect for grades 7 and up. *Includes a digital paperless version of the practice sheet. 1) Practice sheet in which students use a diagram to label the organelles of a plant cell and an animal cell, followed by 5 questions (2.5 pages)2) Laboratory exerci. Anatomy and Physiology: Parts of a Human Cell - Visible Body The nucleus is a large organelle that contains the cell's genetic information. Most cells have only one nucleus, but some have more than one, and others—like mature red blood cells—don't have one at all. Within the nucleus is a spherical body known as the nucleolus, which contains clusters of protein, DNA, and RNA. Nucleus and ribosomes (article) | Khan Academy The nucleus. The nucleus (plural, nuclei) houses the cell's genetic material, or DNA, and is also the site of synthesis for ribosomes, the cellular machines that assemble proteins. Inside the nucleus, chromatin (DNA wrapped around proteins, described further below) is stored in a gel-like substance called nucleoplasm. Cellular organelles and structure (article) | Khan Academy There are two main types of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotes are cells that do not have membrane bound nuclei, whereas eukaryotes do. The rest of our discussion will strictly be on eukaryotes. Think about what a factory needs in order to function effectively.
Labeling a Cell Diagram | Quizlet The command center of the cell. It controls cell's activity. Location Term Cytoplasm Definition A jelly-like substance that fills the cell. All of the cell's organelles are located here. Location Term Vacuoles Definition The storage facilities for the cell. They store food or waste that will be used of gotten rid of later.














![Control & Coordination] Label the parts of a neuron in the ...](https://d1avenlh0i1xmr.cloudfront.net/03e90282-e877-422b-b0a5-8b2bb7ef2342/label-the-parts-ofa-neuron---teachoo.jpg)



Post a Comment for "45 label parts of a cell"